How high school students perform on Connecticut’s state test is a strong predictor of their future success in college, according to one of the first studies of its kind.
The study, “First Steps: An Evaluation of the Success of Connecticut Students Beyond High School,” tracked 10th graders who took the Connecticut Academic Performance Test in 1996 through 2005. It examines the relationship between seven measures of success and those students’ CAPT scores and their scores on the SAT college-admissions exam.
Read a summary of “First Steps: An Evaluation of the Success of Connecticut Students Beyond High School,” posted by the Nellie Mae Education Foundation, which helped fund the study.
For example, it found that students who scored higher on the state test as sophomores took fewer remedial English and math courses in college, took and passed more credits per semester, had higher grade point averages, and were more likely to earn a degree than their lower-scoring peers. They also were more likely to enroll in college soon after graduation.
The study also found the CAPT was as good as, and in a few instances better than, the SAT at predicting college success. In most instances, though, the researchers found that both tests were strong, independent predictors of college success, suggesting that the exams may be measuring different aspects of math and language arts skills.
On a majority of measures, both the Connecticut Academic Performance Test and the SAT are sound, independent predictors of success in college.
*Click image to enlarge
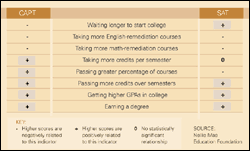
“It certainly provides evidence that these skills are important, reasonable, and challenging, and ones which our students really ought to acquire in order to be able to do really well in postsecondary education,” said Betty J. Sternberg, the state commissioner of education.
The study’s findings are particularly important because many experts are exhorting states to base their high school exit standards more closely on the skills students need to succeed in future education and work. Although nearly half the states require students to pass exams based on their standards to earn a diploma, few have demonstrated the tests accurately measure what students need to know and be able to do to succeed after high school.
In Connecticut, students’ CAPT scores go on their high school transcripts. And, starting with this year’s graduating class, students must show they have mastered the skills the test measures. It’s up to each district to determine the various ways students may demonstrate those skills, including achieving a minimum score on the exam. “Colleges, at least in Connecticut, would be very foolish not to take into consideration CAPT exam results” in making admissions and placement decisions, said Stephen P. Coelen, an economist at the University of Connecticut. He is a co-author of the study with Joseph Berger, the acting director of the Center for Education Policy at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
“One of the most striking results,” Mr. Coelen said, was that students’ scores on the CAPT English and math exams were “nearly perfect predictors” of the need for remedial classes in those subjects once a student arrived in college. Yet he cautioned against substituting the CAPT for the SAT because both are strong, independent predictors of college success, and some students do well on one exam and not the other.
“Certainly, I would never use any test as a sole criterion to make an admissions decision,” said Commissioner Sternberg, “but clearly, this test can be used for that purpose, and also should be used in high schools as we counsel youngsters for what it is they think they want to do.”
A handful of states—including Maine and Michigan—have dropped their state high school tests in favor of requiring all students to take a college-admissions exam, or are considering doing so. At a minimum, Mr. Coelen suggested, states should conduct a similar analysis before making such decisions.
State Brain Drain
The Quincy, Mass.-based Nellie Mae Education Foundation, the Connecticut Department of Education, the Connecticut Department of Higher Education, the Connecticut State University System, and the New England office of the College Board jointly paid for the study.
The analysis also found that of Connecticut high school students going on to college, more than half go out of state, including many of those who score the highest on the state exam.
“This is a group likely to enter the Connecticut labor force in smaller proportions than those who stay in Connecticut for college,” notes the report, and represents a potential brain drain for the state.
Equally troubling, nearly 10 percent of the highest-scoring CAPT students in 1996—or as many as 300 students in the cohort—never entered college at all. “That’s disturbing,” said Ms. Sternberg. “I want to probe that more.”
Among other steps, the report recommends that the state’s flagship institution, the University of Connecticut, add space and improve outreach to attract high school graduates leaving the state, and that the remaining state institutions establish programs to attract students not now continuing their education after high school.




