The U.S. Department of Education announced a dozen more grants last week for schools and districts willing to link the pay of teachers and principals to student test scores.
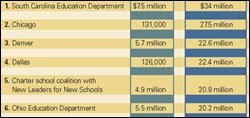
Grant winners include the South Carolina education department, several large urban school systems that have already experimented with nontraditional teacher pay, a nonprofit group that trains aspiring principals in urban districts, and a California charter school.
The U.S. Department of Education has announced recipients of its first round of Teacher Incentive Fund grants. Congress has appropriated funding for the first year only.
*Click image to see the full chart.
SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education
The remaining three awards in a round that is to dole out $43 million from the new Teacher Incentive Fund are expected to come by this week. The latest announcements trickled out throughout the week.
The Education Department has $99 million in the fund for fiscal 2006, but officials said late last month that they would hold a second competition because so many of the roughly 60 applications needed improvement. After providing technical assistance to applicants, officials will award the remaining money in the spring, they said. (“Many Teacher Incentive Fund Applications Rejected,” Nov. 1, 2006.)
Ohio, the only state education department besides South Carolina’s to get a grant in this cycle, will receive $5.5 million for the year, officials announced late last month. The state is expected to get $20 million over five years.
The grants all cover a five-year period, but whether the money is forthcoming will depend both on the federal budget and the grantees’ performance.
The fund requires that the pay innovations be targeted at schools where at least 30 percent of the children are poor. The changes are meant to raise the overall effectiveness of teachers and principals in such schools, in part by professional development and in part by better recruitment and retention measures.
Education Department officials said that applicants were allowed to sketch a plan that rewarded teachers with extra money either on the basis of their own students’ achievement, the school’s overall progress, or both.
“We challenged the applicants to propose which [approach] they felt was best,” said an official who did not wish to be named. “Most of them did a combination.”
TAP Expanded
South Carolina, which stands to get $34 million over five years from the fund, plans to use much of the money to increase the number of schools using the Teacher Advancement Program, a school improvement model that is focused around paying teachers for different levels of accomplishment. The state now has about 16 schools using TAP, an offshoot of the Milken Family Foundation, located in Santa Monica, Calif.
With the grant, 23 more schools are expected to join TAP—though they will be able to pay higher bonuses for raising student achievement than the original schools can, said Jason Culbertson, who will direct the grant. “Master” teachers, who take on professional-development duties, could make as much as an extra $20,000 annually, according to the director.
Grant money will also go to stepped-up recruiting for teachers, especially for TAP schools, including an advertising campaign and out-of-state teacher job fairs, Mr. Culbertson said.
A second grant—to the Eagle County, Colo., school district—will also expand an existing TAP program, in part by increasing performance incentives in the schools that are the hardest to staff.
Denver plans to build on its widely noted success in revamping how teachers are paid to change the compensation system for principals. The five-year, $22.6 million grant would also go to producing better data systems for measuring student academic growth, measurements that would be used for both teachers and principals, said Superintendent Michael F. Bennet.
The teacher pay plan—which is voluntary for all but teachers new to the district—has so far drawn almost 1,700 of the district’s 4,200 teachers. It was also endorsed last year by Denver voters, who voted to increase their taxes by $25 million annually to pay for the plan.
A survey of principals and assistant principals last spring found that about two in three “favored or strongly favored” a pay plan similar to the teachers’.
“It’s nice to have the joint work of the [teachers’] union and the administration recognized by this grant as significant,” Mr. Bennet said. “I hope it gives people confidence … to depart from the status quo.”
Effective Practices
Three grants will go to partnerships led by New Leaders for New Schools, a New York City-based group that trains prospective principals for urban schools. The partners are a coalition of charter schools, the Memphis, Tenn., school district, and the District of Columbia schools.
In addition to helping the coalition and the District design new pay systems for teachers and principals, New Leaders plans to use money from the grants for an ambitious project to help educators do their jobs better. The Effective Practice Incentive Fund will devise ways to research and then share effective practices using Web-based interactive multimedia and visits to designated schools, according to Jon Schnur, the chief executive officer of the group. The concept includes compensation for high-performing educators who contribute to the practice network.
Houston, meanwhile, will use its $4 million grant for the current year to write bigger bonus checks than had been expected under a plan approved by its school board in January. The plan provides for the extra money to go to teachers who produce better-than-average increases in student test scores, either in their classrooms or in some cases as part of a faculty.





