A 17-year-old girl in upstate New York is forced into sex by a male teacher. Instead of sympathy, the student gets harassed for causing trouble for a popular teacher, threatened, and pushed around by other girls. Just six weeks before graduation, she quits school.
A 17-year-old boy in Colorado is seduced by his attractive female teacher. A neighbor tells the teenager’s mom it was a sexual conquest like “climbing Mount Everest.” He has to hide from the crush of media attention.
They are crimes and abuses, but often they’re treated as entertainment. Girls are pressed into the role of seducer or naive victim. Boys are seen as studs. Sexual misconduct by teachers is remarkably common in American schools, a new Associated Press investigation shows. But how Americans react to it is deeply split depending on the victim’s gender.
“Hollywood, they think it’s such a hot thing when a guy gets laid at a young age. I tell you, it’s not a hot thing,” says Jeff Pickthorn, who speaks from experience. He was 12 when he began having sex with his 7th grade teacher, who was 24. “They say that guy’s lucky. I say, no, he’s not lucky at all.”
At the time, Mr. Pickthorn might have agreed with them. For several months, he had sex with his teacher, until his parents found out and the teacher was pressured to resign. It left him “with no boundaries,” he says now at 54, his life marred by affairs, gambling, and ruined marriages.
Media Fascination
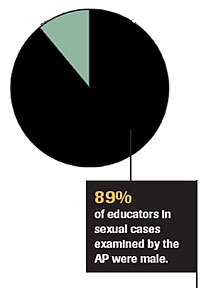
The AP’s survey of five years of state disciplinary actions against teachers found 2,570 educators were punished for sexual misconduct.
In the cases where the victim’s gender was clear, the large proportion were female. Almost nine out of 10 of the offenders were male.
But the boys who are drawn into sexual relationships with their female teachers get an overwhelming amount of attention, especially when the woman is attractive. They’re the subject of heavy news coverage, jokes from late-night TV comics, Web sites with photos, videos, and more.
What’s more likely to be described as rape or sexual abuse when the victim is female turns into a “tryst” or a “sexual liaison” when the perpetrator is female and the victim is male.
SOURCES: AP state bureaus’ research J. Parsons, N. Rapp—AP
“Prosecutors try hard not to treat these cases differently and not to apply any kind of double standard. But there are some very real double standards in society that affect how these cases will be accepted by jurors and judges,” says Michael Sinacore, an assistant state attorney in Tampa, Fla.
He prosecuted Debra Lafave, a former Florida middle school teacher who admitted to having sex with a 14-year-old male student. Public attention paid to the 25-year-old blond newlywed quickly went “off the charts,” Mr. Sinacore says, after photos surfaced on the Internet of her on a motorcycle in a bikini.
“There’s something wrong with making a celebrity out of someone accused of a sex crime,” he said.
Ultimately, the victim’s family sought to avoid a trial because of all the media attention. Ms. Lafave pleaded guilty to lewd and lascivious battery and got house arrest and probation.
The earlier case of Mary Kay Letourneau mesmerized tabloids and television. A married mother of four, she had two children by a student. She went to prison but later married the student, by then 21, after she got out.
Colorado high school teacher Carrie McCandless got 45 days behind bars for unlawful sexual contact with a 17-year-old male student. Not knowing the victim was her son, a friend remarked to the teenager’s mother that having sex with Ms. McCandless would be like “climbing Mount Everest” for any boy.
In contrast, the case of teacher Kevin Poppleton in upstate New York got almost no media attention. His 17-year-old victim, identified as Amanda C. in state records, said Mr. Poppleton threatened to kill her if she talked and “other girls would scream and yell at her and push her around the locker room.” His license was revoked.
Research on Attitudes
Students are traumatized by abuse cases, communities shaken. Yet the public imagination seizes on the idea.
Look at the way pop culture presents teacher-student sex with a wink and a nod: the 1984 Van Halen song “Hot for Teacher”; the 1998 trash-noir movie “Wild Things” about a male high school teacher with two manipulative female students; this year’s hit cable-TV show “Entourage,” in which one of the male characters brags about having sex with a high school teacher.

The roots run deep, at least to the medieval tale of Abelard and Heloise, a scholar who fathers a child with his beloved student.
Approving attitudes can even be found in the courts.
“It’s just something between two people that clicked beyond the teacher-student relationship,” a New Jersey judge said as he dismissed prison time for a teacher who admitted having sex with a 13-year-old student. “I really don’t see the harm that was done, and certainly society doesn’t need to be worried.”
Judge Bruce A. Gaeta was later reprimanded, but at least one academic report found that his view is common.
A 2004 University of Buffalo study gauged perceptions of teacher-student sex. It found that a female teacher with a male student was most often seen as a “normal part of growing up,” and respondents were less likely to conclude that the teacher should lose her license. But male respondents, in marked contrast to women, were more likely to see positive aspects in those relationships and less likely to see long-term damage.
Psychologists who treat boys say they suffer doubly: from the abuse itself, and from the view that they were lucky.
“A boy is likely, with a female teacher, to claim that it wasn’t a problem, it wasn’t molestation, it wasn’t abuse, he wasn’t hurt by it,” says Richard Gartner, a New York psychologist and the author of the 2005 book Beyond Betrayal: Taking Charge of Your Life After Boyhood Sexual Abuse. Recognition of the damage doesn’t usually occur until the man is in his 30s, 40s, or later, he said.

Read more about this series, “A Lingering Shame: Sexual Abuse of Students by School Employees.” The collection includes a new Associated Press series on the issue, as well as special Education Week coverage.
That damage varies widely, depending on the victim’s age, the abuse itself, and the sexual orientation of the boy and of the abuser, Mr. Gartner says. Victims often report addictive behavior and compulsive disorders, from gambling to sex to substance abuse, he says.
Boy or girl, victims often end up with relationships framed in terms of power and control, not affection.
But boys’ pain is overlooked. “In our society, we’re socialized to think that men aren’t victims, that that’s the province of women,” Mr. Gartner says. “To say that you are a victim and particularly a sexual victim, for many boys and men, is to say that you’re not entirely a man.”




