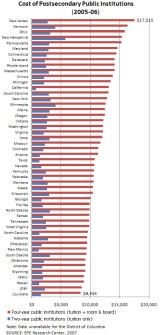
Few would dispute the economic, educational, and social advantages a college education can offer. Those benefits, however, must be weighed against the costs of postsecondary education, which have risen significantly in recent years. Quality Counts 2007 reported an analysis of college costs based on data from the federal Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System. In the 2005-06 school year, the average annual cost for a four-year public institution of higher education was $11,894. That amount—which includes tuition, room, and board—is equal to about one-fifth of a typical American family’s annual income. However, college costs varied significantly from state to state. The lowest cost per year for four-year public institutions ($8,344) was found in Louisiana. New Jersey weighed in with the highest costs, at $17,515. Two-year public institutions represent a substantially more affordable higher-education alternative, with an average tuition cost of $1,939 nationwide. At just $718 per year, California had the lowest tuition cost for two-year public institutions; New Hampshire had the highest price tag at $5,719.
For more state-by-state data on postsecondary costs and other topics, search the EPE Research Center’s Education Counts database.