For the first time, state spending on Medicaid soon may grow larger than state spending on K-12 education, says a report released last week by the nation’s state budget officers.
Primary and secondary education accounted for the largest category of overall state spending in fiscal 2003, according to the annual expenditure report from the Washington-based National Association of State Budget Officers.
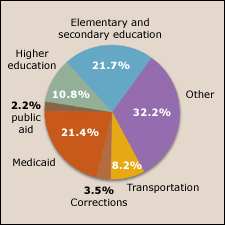
Medicaid spending totaled 21.4 percent of all state spending in fiscal 2003, including federal funds, compared with 21.7 percent for K-12 education. But Medicaid costs were expected to overtake K-12 education in fiscal 2004, according to the budget officers’ projections.
The growth in state spending for Medicaid shows the tremendous pressure on states in that area, and threatens their ability to spend money on other important areas such as education, several observers said last week.
Medicaid spending by states was up 8 percent nationally in fiscal 2003, compared with 6.4 percent in spending growth for K-12 education, and 3.2 percent for higher education.
The “2003 State Expenditure Report” is available online from the National Association of State Budget Officers. (Requires Adobe’s Acrobat Reader.)
“It’s the 800-pound gorilla of state budgets,” said Nick Samuels, a fiscal analyst for the state budget officers and the chief author of the group’s annual report. “That wedge of the pie that is Medicaid has just become larger faster than anything else.”
Increased costs for long-term care in nursing homes and other health-related facilities, higher costs for medicine, and a growing awareness of Medicaid eligibility among poor families are some of the reasons for the increase in Medicaid costs, experts said.
Medicaid costs have already hindered some states from approving new education programs and contributed to major overall budget cuts in recent years, observers added.
“While states have gone to great lengths to hold harmless K-12 education, the fact is that if K-12 is going to grow . . . other pieces of the pie” must shrink, Mr. Samuels said.
Raymond C. Scheppach, the executive director of the Washington-based National Governors Association, said many governors want Congress to help states pay for two of the most costly groups covered by Medicaid: the elderly and poor who qualify for both federal and state health reimbursements.
“It’s scary,” said Mr. Scheppach, who is an economist. “This is seen as an entitlement, and education is discretionary. And so going forward, you’re going to find Medicaid is going to trump education.”
Tough Choices
The state budget officers’ projections for fiscal 2004 spending show that 21 states likely will have spent a higher percentage of their overall budgets on Medicaid than on K-12 schools. The overall spending includes federal dollars, which usually pay slightly more than half of Medicaid expenses.
According to estimates for fiscal 2004, which ended June 30 for most states, Tennessee spent 33 percent of its overall budget on Medicaid—the highest percentage of any state. Maine, Missouri, and Pennsylvania are also among the states that spent higher-than-average percentages of state budgets on Medicaid in fiscal 2004, according to the report’s estimates.
Budget Trends
SOURCE: National Association of State Budget Offices
State Medicaid costs vary greatly depending on the size of the senior population, immigrant groups, and levels of poverty in rural and urban areas.
Some states are trying to curb the increasing Medicaid costs, said Arturo Perez, a fiscal analyst for the Denver-based National Conference of State Legislatures.
Colorado, for example, has cut legal immigrants from Medicaid rolls, Mr. Perez said. States are also retracting some extra benefits that were expanded for Medicaid recipients when the economy boom ed in the 1990s, he said.
Cutting back services, however, is rarely attractive to state lawmakers, he added.
Scott Pattison, the executive director of the state budget officers’ group, said K-12 education has been protected from cuts resulting directly from Medicaid in most states. But education and other areas could bear the brunt of future budget limitations caused, at least in part, from rising Medicaid costs. “What happens to other areas of state government, whether it’s mental-health care or state parks?” Mr. Pattison asked.




